Are you good with numbers and interested in finance? A career in taxation could be your perfect fit!
A sum of money paid to the government by an individual or a business is a tax. Taxation is a pillar of the economy, the revenue generated by the amount helps the government work on its responsibilities in providing various services to its citizens. With the emerging trends globally the scope of taxation is widely broadening its horizons in India. This presents a wealth of career options for professionals skilled in tax, auditing, and financial management.
This blog will help you discover the scope of taxation in India, career opportunities and roles in taxation, growth prospects, and how to get started with it. Additionally, we will also discuss how Inspiria Knowledge Campus’s BBA in Accountancy, Taxation & Auditing can equip you with skills to achieve your career goals.
What is Taxation?
Definition and Importance of Taxation
Taxation is the primary source of government revenue which makes it possible to finance human resources, infrastructures, and provisions for their people and services. It involves the mandatory collection of amounts from all individuals, businesses, and institutions based on their income, consumption, or assets.
Without a proper tax system government would struggle to run any of the healthcare services, transportation, education, military, and law enforcement. It helps to moderate inflation, minimize income inequality, and stimulate corporate growth through incentives. Furthermore, taxation promotes sustainable development by subsidizing environmental efforts and welfare programs, resulting in a balanced and progressive economy.

Types of Taxes in India
There are two different types of taxes which function differently,
Direct Taxes:
These are the taxes that you pay directly to the government. These taxes are imposed based on higher salaries, and valuable assets. The responsibility of the tax has to be completed by the person to whom the tax has been levied and not by any other.
Direct taxes can be further divided into three categories.
- Income Tax:- It is the most common example of a direct tax. The central government of India levies it based on the income of a person or a business generated on a yearly basis.
- Corporate Tax:- Often known as corporation tax or company tax, is a sort of direct tax applied on the profits or capital of corporations and other similar legal entities.The tax is often levied at the national level, although it may also be imposed at the state or local levels in some nations.
- Wealth Tax:- It is a direct tax aimed at reducing wealth inequality. It is levied on the net worth of extremely wealthy individuals, corporations, and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs). It was removed and replaced with a 2% surcharge levy.
Indirect Taxes:
An indirect tax is a type of taxation in which the tax is collected by an intermediary, such as a manufacturer or retailer, and then passed on to the customer via the cost of an item or service. While the entity collects the tax, the customer ultimately absorbs the expense through higher prices.
Indirect taxes can also be divided into three categories.
- GST:- Also known as Goods and Services Tax, is an indirect tax levied in India on the sale of goods and services. GST, or value-added tax, is levied at each stage of the supply chain based on the exact amount of value added.
- Customs Duty:- It is the levy placed on products when they are carried across international boundaries. In plain terms, it is the tax imposed on the import and export of goods.
- Excise Duty:- A type of tax levied on goods for manufacturing, licensing, and sale. Excise duty is an indirect tax paid to the government of India by producers of products. It is the opposite of customs duty in that it applies to goods created domestically in the country.
Scope of Taxation in India
Increasing Demand for Tax Professionals
India’s growing economy and frequently changing tax regulations and compliance needs have led to the demand for professionals who are specialists in this field. The increasing complexity of tax legislation and shifting compliance requirements have created a demand for tax experts, notably GST specialists, tax auditors, and corporate tax planners. Businesses seek expertise to negotiate tax rules, optimize obligations, and maintain regulatory compliance, making tax consulting a profitable and in-demand job path.
Career Growth Potential
Government tax reforms, such as the implementation of GST and regular updates to tax rules, have greatly improved employment prospects in the financial and corporate sectors. Businesses and individuals will need tax professionals to help them navigate these changes and ensure compliance and efficient tax planning.
Simultaneously, AI and automation are revolutionizing tax operations through routine computations and data analysis. However, this transition has increased the demand for taxation professionals capable of interpreting complicated tax legislation, providing strategic insights, and overseeing detailed financial planning.
Global Opportunities in Taxation
Taxation is an internationally significant field that provides possibilities for experts to work with multinational corporations (MNCs), financial institutions, and consulting organizations. International taxation positions, such as transfer pricing specialists and cross-border tax consultants, are in great demand as organizations grow abroad.
Furthermore, Indian tax professionals are becoming increasingly sought after in overseas markets as a result of India’s broad tax treaties and growing economic power.Their skill in dealing with complex tax systems, compliance rules, and international trade laws makes them significant assets in global financial centers.

Career Opportunities in Taxation in India
A career in taxation offers diverse opportunities, ranging from advisory and compliance roles to auditing, legal representation, and policy development. With tax laws constantly evolving, professionals in this field play a vital role in ensuring financial transparency, regulatory compliance, and strategic tax planning for businesses and individuals alike. Let’s explore some of the most trending and lucrative career opportunities in Taxation.
Tax Consultant:-
Tax Consultants are the advisors for businesses and individuals helping them on tax-saving strategies while ensuring compliance with tax laws. They have a deep understanding of tax laws and accounting principles and are aware of all the trends providing the best guidelines.
They can begin their career starting their work with the Indian Revenue Service (IRS) or work as a Chartered Accountant and Company Secretary. They can also be hired by renowned corporate firms, corporate clients, startups, and individual taxpayers ensuring they have a few years of experience.
Tax Analyst:-
A tax analyst prepares and reviews tax returns, and ensures compliance with laws. Tax analyst utilizes tax information and makes strategies so that the company remains competitive.
Multinational Corporations (MNCs), financial institutions, and accounting firms employ tax analysts, who are essential to risk management, regulatory reporting, and tax planning. Their knowledge aids companies in navigating intricate tax arrangements and upholding adherence to changing taxes.
GST Practitioner:-
An expert in Goods and Services Tax (GST) compliance, a GST practitioner helps companies with tax returns, filings, and advice services. They assist in resolving compliance concerns, ensuring accurate tax payments, and keeping abreast of changing GST requirements.
The need for GST practitioners has increased with the introduction of GST in India since companies need professional assistance to handle the intricacies of the tax system. Strong employment opportunities in accounting companies, consulting services, and corporate tax departments are provided by this position.
Tax Accountant:-
Maintaining financial records, creating tax returns, and making sure that both people and businesses file their taxes accurately are the duties of a tax accountant. While maintaining adherence to tax regulations, they evaluate financial data, find tax deductions, and help reduce tax obligations.
In corporate finance departments, audit firms, and chartered accounting (CA) businesses, tax accountants are crucial. In the ever-changing tax landscape, their knowledge is essential for regulatory reporting, tax audits, and financial planning.
Income Tax Officer:-
An Income Tax Officer (ITO) is a government official who works for the Income Tax Department, assessing and collecting taxes, conducting audits, and investigating tax evasion cases. They assure income tax compliance and contribute significantly to the country’s financial stability.
To become an Income Tax Officer, individuals must pass competitive exams like as the SC CGL (Staff Selection Commission – Combined Graduate Level Exam) and UPSC (Union Public Service Commission). This important position provides employment security, professional development, and the opportunity to contribute to the nation’s economic system.
Auditor:-
An auditor is responsible for assuring financial transparency and tax compliance by scrutinizing financial records, checking tax filings, and discovering anomalies or fraud. They assist enterprises and organizations in maintaining accurate financial reporting and ensuring compliance with regulatory obligations.
Auditors conduct both internal and external audits for commercial companies, government agencies, and financial institutions. They work with private firms and government bodies as their knowledge is critical for risk assessment, financial planning, and ensuring the integrity of company and government budgets.
Industries Hiring Tax Professionals
Industries Hiring Tax Professionals Tax specialists are in great demand across sectors because taxes are so important in financial management and regulatory compliance. Some important industries that actively seek tax professionals include:
- Corporate Firms – Corporate firms that provide tax planning and compliance services, ensuring that corporations follow tax requirements while optimizing liability.
- Banks & Financial Institutions – Banks and financial institutions require expertise in investment taxation, wealth management, and regulatory reporting.
- Government Sector – Positions in the Income Tax Department, GST offices, and other tax regulating agencies provide secure employment possibilities.
- CA & Auditing Firms – Hire tax specialists for auditing, financial reporting, and consulting services to help businesses and individuals comply with tax laws Tax filing, audits, and compliance.
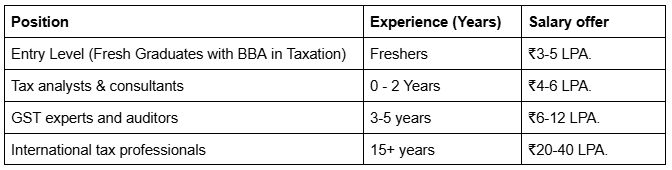
Salary & Growth Prospects in Taxation Careers
Skills Required for a Successful Career in Taxation
Technical Skills
A taxation professional who understands tax laws, GST, and compliance requirements must have good analytical skills to grasp regulations and ensure appropriate tax filings. Accounting software proficiency, such as Tally, SAP, and QuickBooks, is required for financial record management, tax return preparation, and report generation. They should be able to handle GST filings, tax audits, and compliance procedures while keeping up with changing tax legislation.
Soft Skills
A taxation expert must have good analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities to interpret complicated tax regulations, discover compliance concerns, and design innovative tax-saving solutions. Effective communication and negotiation skills are essential for explaining tax legislation to clients, coordinating with tax authorities, and settling issues.
Continuous Learning & Certifications
A competent tax professional must prioritize ongoing learning to keep up with changing tax laws and financial rules. Earning certifications such as CA, CMA, ACCA, or CPA improves competence and career chances by demonstrating advanced knowledge of tax and accounting. Furthermore, getting government certifications such as GST Practitioner and Tax Auditor qualifications boosts credibility and enables professionals to provide specialized tax services.

How to Start a Career in Taxation?
Step 1: Educational Qualifications
- Pursue a degree in commerce, finance, or taxation (e.g., BCom, BBA, or BSc in Finance).
- Consider professional courses like CA, CMA, or CS.
Step 2: Certifications
Enrol in GST certification programs or diploma courses in taxation to improve your skills. These certifications can help you advance your profession, develop your practical understanding, and keep up with changing tax legislation.
Step 3: Internships and Practical Experience
Gain hands-on experience through internships or entry-level jobs to apply theory learnings to real-life situations. Various types of internships and practical experiences not only help you add more to your resume but also bring growth to your career.
Step 4: Networking
Join professional organizations like the ICAI and attend industry events to stay current on tax legislation and compliance developments. Networking with professionals, taking workshops, and participating in professional forums can help you advance your career and gain an understanding of taxation.
How Inspiria Knowledge Campus Can Help?
The BBA curriculum at Inspiria Knowledge Campus is designed to give students a solid foundation in taxation, auditing, and accounting. The curriculum combines theoretical knowledge with practical applications, ensuring that students learn the necessary abilities for real-world financial and taxation responsibilities. With a focus on GST compliance, financial reporting, and tax planning, the curriculum prepares students for employment in accounting and finance.








